Table of Contents
Exploring Millet: Is Millet Gluten-Free?
In recent years, there has been a surge of interest in gluten-free diets, with many individuals turning to alternatives like millet for their nutritional needs. But the question remains: Is millet truly gluten-free? Let’s delve deeper into this trending topic and uncover the truth ”Is Millet Gluten-Free”?
Understanding Millet: A Versatile Grain
A millet, often referred to as a whole grain, is a diverse group of small-seeded grasses that have been cultivated for thousands of years, primarily in Africa and Asia. Its cultivation dates back to ancient civilizations, where it served as a staple food source due to its resilience and adaptability to various climates.
This ancient grain comes in various types, each with its unique characteristics and culinary uses. Pearl millet, for instance, is commonly grown in Africa and India and is known for its drought tolerance, while foxtail millet is prevalent in East Asia and is prized for its nutritional value. Other varieties include Finger Millet, Proso Millet, Kodo Millet, Browntop Millet, and Barnyard millet, each offering its distinct flavor and texture.
The Gluten-Free Status of Millet:
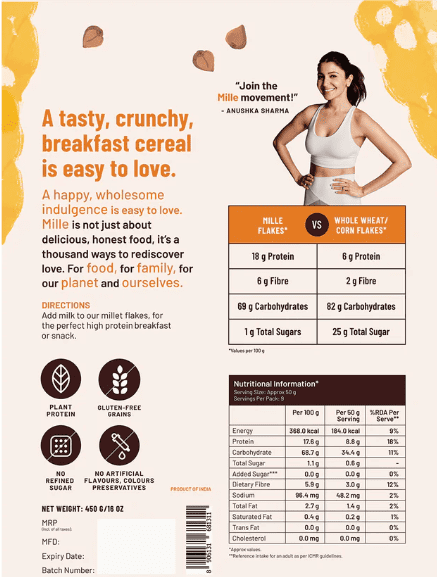
Yes, millet in its natural form is gluten-free. These small-seeded grasses are harvested for grains and are used in a wide variety of ways. Versatile and diverse, millet grains are used in dishes around the world, including flatbreads, porridges, drinks, pilafs, breads, and more. Millet can also be made into alcoholic beverages, such as millet beer. Additionally, millet is used in livestock feed and birdseed, so be sure the millet you purchase is for human consumption as millet sold for animals has its indigestible hull intact.
For individuals with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease, millet presents a safe and nutritious alternative to gluten-containing grains like wheat, barley, and rye.
Celiac disease is a chronic autoimmune disorder provoked by the ingestion of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. When individuals with celiac disease consume gluten, their immune system mistakenly identifies it as a threat and launches an attack against the small intestine. This immune response damages the villi, tiny finger-like projections lining the intestine responsible for absorbing nutrients from food. As a consequence, the impaired villi hinder the absorption of essential nutrients, resulting in malnourishment and a spectrum of associated health complications.
Thus, celiac disease necessitates strict adherence to a gluten-free diet to manage symptoms and prevent further intestinal damage.
Is Millet Flour Gluten-free?
Wonderfully, millet flour is a gluten-free option, offering a boon for those adhering to gluten-free diets. Its versatility makes it an excellent choice for crafting a variety of gluten-free delicacies, ranging from bread and pasta to cakes, pies, muffins, and even pizza. However, it’s important to exercise caution: certain millet flours may be blended or come into contact with gluten-containing grains during processing. Thus, it’s prudent to diligently scrutinize product labels when purchasing millet flour to ensure that it is indeed free from gluten.
Nutritional Benefits of Millet:
Beyond its gluten-free status, millet boasts an impressive nutritional profile, making it a valuable addition to any diet. It is rich in essential nutrients such as fiber, vitamins, and minerals, including magnesium, phosphorus, and iron. Additionally, millet is a good source of antioxidants and phytonutrients, which have been linked to various health benefits.
One notable characteristic of millet is its high fiber content, which promotes digestive health by supporting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Fiber also helps regulate blood sugar levels, making millet a suitable choice for individuals with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels.
Furthermore, millet is a good source of protein, particularly for individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets. While it may not provide as much protein as animal-based sources, incorporating millet into meals can help contribute to overall protein intake and promote satiety.
Culinary Uses and Preparation Tips:
Incorporating millet into your diet is easy and versatile. This ancient grain can be cooked and enjoyed in various ways, adding texture and flavor to a wide range of dishes. Here are some popular culinary uses of millet:
- Flatbreads: Millet flour can be used to make gluten-free flatbreads, pancakes, or wraps. These alternatives offer a nutritious and flavorful option for individuals avoiding gluten.
- Porridges: Cooked millet can be used as a base for sweet or savory porridges, similar to oatmeal. Simply simmer millet in water or milk until tender, then add your favorite toppings such as fruits, nuts, or spices.

- Pilafs and Stir-Fries: Millet can be cooked pilaf-style with vegetables, herbs, and spices for a flavorful side dish or main course. It can also be added to stir-fries for added texture and nutrition.
- Breads and Baked Goods: Millet flour can be used in gluten-free baking to make bread, muffins, cookies, and other baked goods. Its mild flavor and fine texture make it an excellent substitute for wheat flour in recipes.
When cooking with millet, it’s essential to rinse the grains thoroughly before cooking to remove any debris or bitter compounds. Additionally, using a ratio of 2 cups of liquid to 1 cup of millet when cooking will ensure a fluffy and tender texture.
Potential Concerns and Considerations:
While millet is generally safe and nutritious for most individuals, there are a few considerations to keep in mind:
- Thyroid Health: Research suggests that millet may contain goitrogens, compounds that can interfere with thyroid function by inhibiting iodine uptake. For individuals with thyroid disease or iodine deficiency, consuming large amounts of millet may exacerbate these conditions. It’s advisable to seek guidance from a healthcare professional if you have concerns about thyroid health and millet consumption.
- Cross-Contamination: Despite being naturally gluten-free, millet products may be at risk of cross-contamination during processing or handling. Manufacturers that process both gluten-containing grains and millet products may inadvertently introduce gluten traces into millet-based foods. Therefore, individuals with severe gluten allergies should exercise caution and opt for certified gluten-free millet products to ensure their safety.
Final Thoughts:
In conclusion, millet is indeed gluten-free, making it a suitable choice for those with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease. Its growing popularity stems not only from its gluten-free status but also from its nutritional richness and versatility in culinary applications. By incorporating millet into their diets, individuals can enjoy a wholesome and satisfying gluten-free alternative that promotes overall health and well-being.
However, it’s essential to approach millet consumption mindfully, considering potential concerns such as thyroid health and cross-contamination. By understanding the benefits and considerations associated with millet, individuals can make informed decisions about including this ancient grain in their diets. Whether enjoyed as a nourishing porridge, a hearty pilaf, or a gluten-free baked good, millet offers a flavorful and nutritious addition to any meal.
Author: Tapas Chandra Roy, A Certified Farm Advisor on Millets, ‘Promoting Millets from Farm to Plate’ and an Author of the book -” Millet Business Ideas-Empowering Millet Startups”. In a mission to take the forgotten grains- Millets to Millions. To remain updated on my blogs on Millets please subscribe to my newsletter and for any queries please feel free to write to [email protected]

